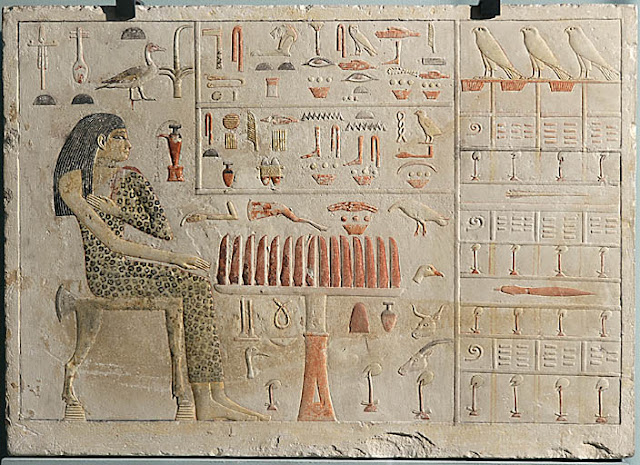
This relief stele from Princess Nefertiabet’s tomb (G 1225) in Giza depicts her and other relatives of the king, including Nefertiabet, daughter of Khufu. She is shown seated, facing to the right, depicted with a long wig and a panther-skin garment.
An offering table before her holds customary reeds and various food items. Below are linen and ointment on the left, and bread, beer, oryx, and bull on the right. A linen list is displayed beside the slab.
Now, I would like to share an excellent description of the discovery of this beautiful ancient artwork by the brilliant Marie Grillot.
The stele of Nefertiabet: from its mastaba in Giza to the Louvre Museum
via égyptophile

Discovered by Montague Ballard in 1902 in mastaba G 1225 at Giza
Entered into the Louvre Museum in 1938 by the gift of L., I. and A. Curtis – E 15591
In 1901-1902, Montague Ballard, a British brewer, obtained an excavation permit at the Giza site. He stayed there for only a very short time, but it was long enough to make some interesting discoveries. In 1902, in the western cemetery, he discovered a mastaba, which would be referenced as G 1225, that notably contained the “Stele of Nefertiabet,” named after its “owner.”
Most of the artefacts discovered during his mission were subsequently dispersed. Three pieces from the mastaba ended up in Arthur Sambon’s collection. They were then put up for sale on May 25, 1914, in Paris by the expert Jacob Hirsch. The stele seems to correspond to the object presented under No. 2 of the “Stone Sculptures of Egyptian Art.” Did it then pass into other hands? In any case, it was later found in the possession of an aesthete and art lover: Atherton Curtis.
Born in New York in 1863, he settled in Paris in 1904, where he “brought and continually increased his collection.” In “La Grande Nubiade,” Christiane Desroches Noblecourt recalls: “Among the most prestigious donors (to the Louvre), not only for the Egyptian department but for all the others, was Atherton Curtis. He wanted to add to his name that of Louise, his first wife, who died prematurely, and that of the second, who was also passionate about all antiquities, Ingeborg.” The stele entered the Louvre in 1938 through the “Curtis Bequest.” It was during the November 8, 1938 meeting of the Council of National Museums that Charles Boreux, Curator of the Department of Egyptian Antiquities, informed “the Council of the immediate gift, by Mr. and Mrs. Atherton Curtis, of three magnificent pieces of sculpture included in the donation subject to usufruct that they made to the Louvre a few months earlier. These are a painted limestone group representing King Amenhotep and Queen Nofertiti, a group from the Old Kingdom, and finally a polychrome bas-relief in the name of Princess Nofritabtj.” He died in 1943, and the stele was then permanently housed at the Louvre, registered under the reference E 15591.
Measuring 37.70 cm high, 52.50 cm wide, and 8.30 cm thick, it is made of painted limestone. It belongs to the category known as “slab stelae,” which are in fact “slabs embedded in the walls of funerary chapels” and which represent the oldest reliefs in Giza.
discovered by Montague Ballard in 1902 in mastaba G 1225 at Giza
entered the Louvre Museum in 1938 by the Donation of L., I. and A. Curtis – E 15591 – photo © 2013 Musée du Louvre / Christian Décamps
While the scene depicted is relatively common in Old Kingdom funerary iconography, its quality and the finesse of its execution remain exceptional. This suggests that it was likely executed in the workshops of Pharaoh Khufu. This could also be explained by the fact that Nefertiabet was either “the daughter or sister of the great pharaoh” or, according to another interpretation, “probably a sister of King Khufu and a daughter of Snefru.”
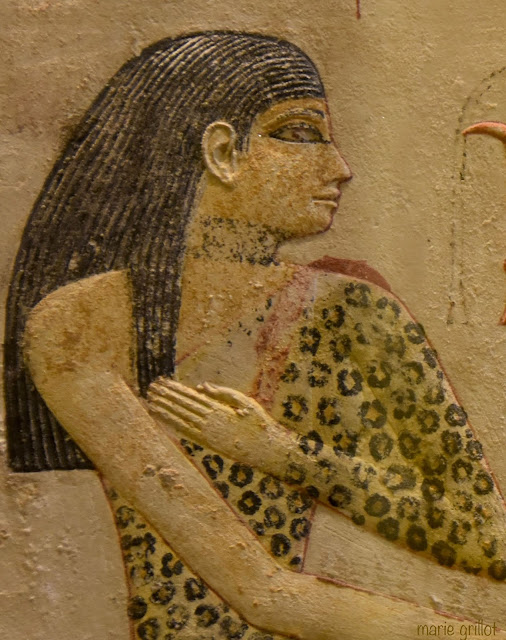
The rectangular surface is surrounded by a plain band standing out in slight relief. Nefertiabet is depicted alone facing her eternal meal. She is on the left side, seated on a delightful bull-legged stool, the back of which is decorated with a papyrus umbel.
Slim, fine, slender, her “yellow skin colour is well preserved,” and she is particularly elegant. Her panther-skin dress is held together, on the left, by “seven red shoulder knots, all applied with paint,” while on the right, the shoulder is bare. The garment stops above the ankles, revealing the bracelets that adorn them, while her bare feet rest flat on the ground.

Discovered by Montague Ballard in 1902 in mastaba G 1225 at Giza
Entered into the Louvre Museum in 1938 by the gift of L., I. and A. Curtis – E 15591
This stele, walled up in the chapel of her tomb in Giza, magically ensured the eternal nourishment of the deceased, a relative of King Khufu.
Her perfectly profiled face is highlighted by a long, black, tripartite wig, which covers a large part of her forehead but leaves her ears visible. Her large eyes are rimmed with kohl, and her nose and mouth are of ideal proportions; only her neck, adorned with a necklace, appears a little short. “The face expresses the ideal of feminine beauty at the time of the pyramids: slightly rounded forehead, fine, straight nose, delicately contoured lips and nostrils, and a rounded throat” (Christiane Ziegler, “Egypt at the Louvre”).
Her left arm rests, hand flat, on her right breast, while her right arm is held alongside her body, hand outstretched towards “a white stone footed tray, placed on a cylindrical terracotta support, and covered with slices of cake with a golden crust and white crumb”.
The quality of the carved and painted hieroglyphs that “document” the stele is of total perfection, as proven by the precision of execution of the libation ewer, the animal heads, and even the birds,…
Above Nefertiabet’s head, “an inscription in large hieroglyphs enhanced with colour specifies her name and title; one will particularly admire the reed and the duck, meaning respectively ‘king’ and ‘daughter’… All around (the pedestal table) hieroglyphic signs and images immortalise the offerings necessary for her survival that the inscription wishes her thousands of: duck with its head cut off; head, foreleg and rib of beef; jug of wine. Above the table, two lines of hieroglyphs, arranged in a frame, list the products of the funerary ritual (incense, ointment, green and black makeup) as well as fruits and drinks: figs, jujubes, carobs, beer, and wine. The entire right-hand side is occupied by lists listing thousands of pieces of fabric, undoubtedly necessary for mummification, with their quality and length, as specified by Christiane Ziegler in the work cited above.
One might rightly wonder how this stele, which dates from 2590-2565 BC and is therefore more than 4,500 years old, has reached us in such a well-preserved state. Here is part of the explanation: “This stele was sealed on the outer wall of its tomb in Giza, at the foot of the Great Pyramid. Later walled up, it was protected from the wear and tear of time and men.
In his study “Slab Stelae of the Giza Necropolis” published in 2003, Peter Der Manuelian specifies however that: “The remains of the original mud-brick chapel have not been preserved and the exact location of the slab stela could not be determined due to the destruction of this part of the mastaba wall by Ballard”…
But at the Louvre, in the heart of the prestigious Parisian museum – precisely on the first floor of the Sully wing, in room 635 dedicated to the Old Kingdom – Nefertiabet remains very much alive, adorned with everything fundamental to ensure her a long, very long eternity…
Sources:
Stele of Nefertiabet
https://collections.louvre.fr/ark:/53355/cl010005261
Jacob Hirsch, Expert, Catalogue of Works of Art and High Curiosities…, Faience…, Saxon Porcelain,… Egyptian and Greek Sculptures…, Persian Manuscripts…, Old Paintings… Forming the Collection of Mr. Arthur Sambon… Sale: May 25-28, 1914, Imprimerie Georges Petit, Paris, 1914
https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k12478139/f12.item.r=tombeau
Charles Boreux, The Atherton Curtis Donation, Bulletin des musées de France, November 1938
http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k58649569/f8.image.r=curtis?rk=21459;2
Christiane Desroches Noblecourt, The Great Nubian or the Journey of an Egyptologist, Stock, 1992
Guillemette Andreu, Marie-Hélène Rutschowscaya, Christiane Ziegler, Ancient Egypt at the Louvre, Hachette, 1997
Christiane Ziegler, Egyptian Art in the Age of the Pyramids, Réunion des musées nationaux, 1999, p. 20, 207-208, notice no. 54.
Peter Der Manuelian, Slab Stelae of the Giza Necropolis, The Peabody Museum of Natural History of Yale University, The University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology, New Haven and Philadelphia, 2003
http://giza.fas.harvard.edu/search-results/?q=1225
Morris L. Bierbrier, Who Was Who in Egyptology, London, Egypt Exploration Society, 2012
Campbell Price, Ancient Egypt, Pocket Museum, Thames & Hudson, 2018


You must be logged in to post a comment.